Contents
A variable is defined as a named piece of computer memory that is used to store a variety of values or data.We can have different types of variables ie they may belong to a particular data type.
Java has two data types:
- Primitive data (e.g., number, character)
- Object data (programmer created types)
And since Java is a strongly typed language, every variable must have a declared data type mentioned above.
In short, variables can be explained in a simple way as:
Imagine bank lockers. There are numerous separate lockers. These lockers can be considered to be the memory slots. You can use one of them, select the type, name them and store values in them. You can modify the values too. And once its job is complete, you discard the value from it and the slot is empty once again.
Rules of declare variables
We can declare variables in Java as follows: 
datatype: Type of data that can be stored in this variable.
variable_name: Name given to the variable.
value: It is the initial value stored in the variable.
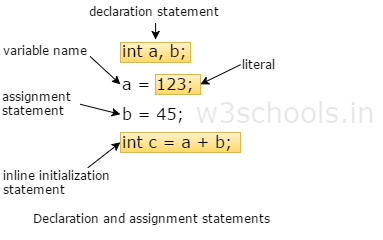
Examples:
float simpleInterest; //Declaring float variable int time = 10, speed = 20; //Declaring and Initializing integer variable char var = 'h'; // Declaring and Initializing character variable
If variables are of the same type, they can be declared together, as follows:
datatype variable1, variable2, ..., variablen;
The variables are separated by commas. For example,
int i, j, k // Declare i, j, and k as int variables
Variables often have initial values. You can declare a variable and initialize it in one step. Consider, for instance, the following code:
int count = 1
This is equivalent to the next two statements:
int count; count = 1;
You can also use a shorthand form to declare and initialize variables of the same type together. For example,
int i = 1, j = 2;
A variable must be declared before it can be assigned a value. A variable declared in a method must be assigned a value before it can be used. Whenever possible, declare a variable and assign its initial value in one step. This will make the program easy to read and avoid programming errors.
Variable Scope means – That limit, as far as the variable can be used.
In Java there are various types of variable scope:
- Local variables
- Instance variables
- Class/Static variables
Local variables
A variable that is declared within the method that is called local variables. It is defined in method or other statements, such as defined and used within the cache block, and outside the block or method, the variable cannot be used.
Instance variables
A non-static variable that is declared within the class but not in the method is called instance variable. Instance variables are related to a specific object; they can access class variables.
Class/Static variables
A variable that is declared with static keyword in a class but not in the method is called static or class variable.
Examples
class A {
int amount = 100; //instance variable
static int pin = 2315; //static variable
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 35; //local variable
}
}
public class Example {
int salary; // Instance Variable
public void show() {
int value = 2; // Local variable
value = value + 10;
System.out.println("The Value is : " + value);
salary = 10000;
System.out.println("The salary is : " + salary);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Example eg = new Example();
eg.show();
}
}
Variable assignment
Variable_Name = value int a = 100; int b; b = 25; // ------> direct assigned variable b = a; // ------> assigned value in term of variable b = a+15; // ------> assigned value as term of expression
Rules to declare a Variable
- Every variable name should start with either alphabets or underscore ( _ ) or dollar ( $ ) symbol.
- No space is allowed in the variable declarations.
- Except underscore ( _ ) no special symbol is allowed in the middle of the variable declaration
- The variable name always should exist on the left-hand side of assignment operators.
- The maximum length of the variable is 64 characters.